Krabi pulsar
Krabi pulsar (PSR B0531+21, NP 0532, PSR J0534+2200) on Krabi udukogus asuv võrdlemisi noor neutrontäht (pulsar), mis tekkis 1054. aastal avastatud supernoova SN 1054 tagajärjel.[1][2][3] 1968. aastal avastatud pulsari näol on tegemist esimese avastatud pulsariga, mis tekkis supernoova jäänukina.[4]

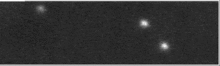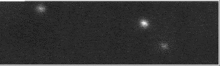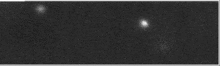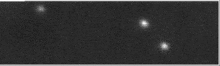
Krabi pulsar on üks vähestest optiliselt avastatud pulsaritest. Selle läbimõõt on umbes 20 kilomeetrit ja see pöörleb umbes 30 korda sekundis (iga 33 millisekundi tagant).[5][6] Täiendaval vaatlemisel on avastatud, et pulsari pöörlemiskiirus aeglustub 38 nanosekundit päevas.[7]
Krabi pulsarit kasutatakse tihti röntgenastronoomias vaatlusseadmete kalibreerimiseks.[8][9]
Viited muuda
| Pildid, videod ja helifailid Commonsis: Krabi pulsar |
- ↑ Frommert, Hartmut & Kronberg, Christine (30. august 2006). "Supernova 1054 - Creation of the Crab Nebula" (inglise keeles). Students for the Exploration and Development of Space. Vaadatud 20. märts 2018.
{{netiviide}}: CS1 hooldus: mitu nime: autorite loend (link) CS1 hooldus: tundmatu keel (link) - ↑ Duyvendak, J. J. L. (1942). "Further Data Bearing on the Identification of the Crab Nebula with the Supernova of 1054 A.D. Part I. The Ancient Oriental Chronicles". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 54: 91. Bibcode:1942PASP...54...91D. DOI:10.1086/125409.
Mayall, N. U.; Oort, Jan Hendrik (1942), "Further Data Bearing on the Identification of the Crab Nebula with the Supernova of 1054 A.D. Part II. The Astronomical Aspects", Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 54: 95, Bibcode:1942PASP...54...95M, DOI:10.1086/125410 - ↑ Brandt, K.; et al. (1983). "Ancient records and the Crab Nebula supernova". The Observatory. 103: 106. Bibcode:1983Obs...103..106B.
- ↑ Zeilik, Michael; Gregory, Stephen A. (1998). "Introductory Astronomy & Astrophysics" (4th ed.). Saunders College Publishing: 369. ISBN 0-03-006228-4.
{{cite journal}}: viitemall journal nõuab parameetrit|journal=(juhend) - ↑ Becker, W.; Aschenbach, B. (1995). Alpar, M.A.; Kızıloğlu, Ü.; van Paradijs, J. (toim-d). "The Lives of the Neutron Stars". Proceedings of the NATO Advanced Study Institute on the Lives of the Neutron Stars. 450. Kluwer Academic: 47. arXiv:astro-ph/9503012. Bibcode:1995ASIC..450...47B. ISBN 0-7923-324-6-6.
{{cite journal}}: viitemall journal nõuab parameetrit|journal=(juhend); eiran parameetrit|chapter=(juhend) - ↑ Leedjärv, Laurits (2012). "Tähed, mis mahuksid Tallinna linna". Horisont. Horisont 2/2012. Originaali arhiivikoopia seisuga 24. märts 2018. Vaadatud 20. märts 2018.
- ↑ Smith, H. E. (Gene) (16. aprill 1999). "Supernovae, Neutron Stars & Pulsars" (inglise keeles). University of California, San Diego Center for Astrophysics & Space Sciences. Vaadatud 20. märts 2018.
{{netiviide}}: CS1 hooldus: tundmatu keel (link) - ↑ Kirsch, Marcus & Briel, U & Burrows, D & Campana, S & Cusumano, Giancarlo & Ebisawa, K & J. Freyberg, M & Guainazzi, Matteo & Haberl, F & Jahoda, K & Kaastra, J & Kretschmar, Peter & Larsson, S & Lubinski, Piotr & Mori, K & Plucinsky, P & Pollock, Andy & Rothschild, R & Sembay, S & Yamamoto, M. (2005). Crab: The standard X-ray candle with all (modern) X-ray satellites. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering. 5898. 22-33. DOI:10.1117/12.616893.
- ↑ Toor, A.; Seward, F. D. (1974). "The Crab Nebula as a calibration source for X-ray astronomy". Astronomical Journal,. 79: 995–999. Bibcode:1974AJ.....79..995T. DOI:10.1086/111643.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 hooldus: üleliigsed kirjavahemärgid (link)